Audi Q3: Side Wall Lettering
Example: Dunlop SP Sport 9000
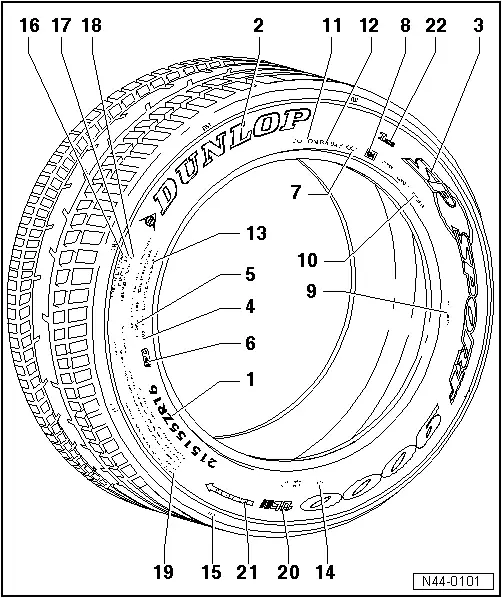
1 - Size Designation (215/55 ZR16)
- Label on PAX tires. Refer to → Chapter "Run-Flat Tire (PAX), Labeling On Sidewall"
2 - Manufacturer (Trade Name)
3 - Tread Designation
4 - Label for Tubeless Tires
5 - Radial - Construction (Radially-Oriented Fibers in Shell)
6 - Note for Versions with "Rim Protection"
7 - Production Date - See Tire Aging
 Note
Note
Retreaded tires also have a label "R" or "Retreated" and the date when it was retreaded instead of the production date.
8 - E number = Approval Number The Tires Fulfill all European Guidelines.
- European guidelines according to ECE-R30, EEC92/93 or ECE - R 117
 Note
Note
- Based on the EU guideline ECE- R117, tires that fulfill the new driving noise limits also have an "S" designation for Sound on the sidewall.
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section up to 185 mm: from 10/01/2009
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section from 185 mm to 215 mm: from 10/01/2010
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section over 215 mm: from 10/01/2011
9 - Production Country - Manufactured in Germany.
10 - Internal Tread Code from Manufacturer
11 - Department of Transportation - the Tires Fulfill the Guidelines of the American Traffic Authorities
12 - Example: Dunlop SP Sport 9000
DOT - identification number code for production plant, tire size and tire version
13 - Maximum Permitted Load (Load Index)
- Table. Refer to → Chapter "Load Rating/Load Index (LI)".
 Note
Note
Additional designation of "Reinforced" or "Extra Load" or "XL" is required for tire load capacity increase
- Reinforced, Extra Load Tires. Refer to → Chapter "Tires, Reinforced, Extra Load"
14 - Number of Layers in the Tread Center and in the Sidewalls and Specification of Material
15 - Position of Tread Wear Indicator (TWI)
16 - Relative Service Life Expectancy - Abrasion Resistance - Refers to a US-Specific Standard Test
17 - Rating of Wet Braking Capability: A, B or C Based on US-Specific Test
18 - Rating of Temperature Stability: A, B or C Based on US-Specific Test
19 - Safety Notes for use or Fitting of Tires
20 - Indication of "Ultralight Construction", Tire is up to 30% Lighter
21 - Specified Running Direction of Tire
22 - Inmetro Label, is Only Required for the Brazilian Market
Tire Dimension Explanation
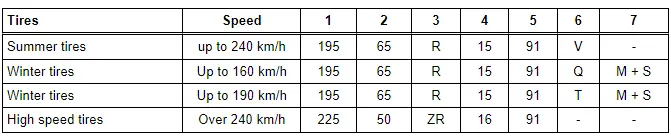
1 - Tire width
2 - Aspect ratio in %
3 - Tire construction code "R" (means radial)
4 - Rim diameter designation
5 - Load index (LI)
6 - Speed Rating
7 - Winter tire/designation for all-season tire
 Note
Note
- A designation required by Audi may also be on the sidewall, such as "R01" and/or "AO". These are approved by Audi and are specially designed for specific Audi models.
- The designation "R01" can vary depending on the model from "R02 or R0...".
 Note
Note
- Based on the EU guideline ECE- R117, tires that fulfill the new driving noise limits also have an "S" designation for Sound on the sidewall.
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section up to 185 mm: from 10/01/2009
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section from 185 mm to 215 mm: from 10/01/2010
- For passenger vehicle tires with a cross section over 215 mm: from 10/01/2011
Run-flat tires, SST (Self Supporting Tire) and PAX have a special designation on the tire sidewall depending on the manufacturer.
Run-Flat Tire (PAX), Labeling On Sidewall
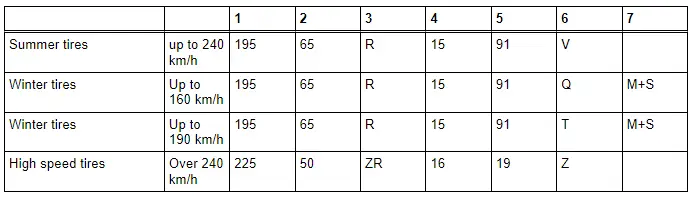
1 - Tire width
2 - Aspect ratio in %
3 - Tire construction code "R" means radial
4 - Rim diameter designation
5 - Load index
6 - Speed Rating
7 - Winter tire/designation for all-season tire
EU Tire Label
Brief Overview - EU Tire Label
Starting on 11/01/2012, tire manufacturers must comply with the new EU Regulation (EG) 1222/2009 (Tire Labeling Regulation).
The Tire Labeling Regulation requires that information pertaining to rolling resistance (fuel efficiency), wet grip and external rolling noise be printed on a uniform EU tire label. The goal of this is to increase safety and ecological and economical road transport efficiency by using tires that are safer, quieter and use less fuel.
The new EU tire label contains concrete information for seven classes from A to G.
There are 3 different categories:
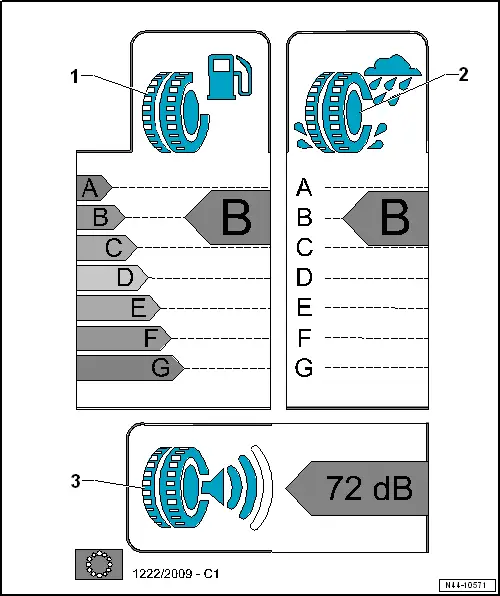
1 - Rolling Resistance
- Explanations.
2 - Wet Grip
- Explanations.
3 - Noise Emission
- Explanations.
EU Tire Label, Purposes
- To reduce fuel usage
- To improve road safety
- To reduce traffic noise
The EU Tire Label Provides the end-user with Information about the tire's Most Important Properties. However, it Does not Provide all Critical Safety Criteria.
- Explaining additional tire properties can exert a sustained influence on the purchasing decision.
- The customer should be made aware of the limited reliability of the label regarding tire properties. For example, the label says nothing about the winter properties on winter tires.
- Tire tests remain important sources of information for dealers and end-users.
The tires test check many other performance factors, including the following:
- Aquaplaning properties
- Driving stability
- Steering precision
- Service life
- Braking properties
- Performance under winter conditions
EU Tire Label, Categories
Rolling Resistance
Rolling Resistance:
- is defined as the amount of energy used by a tire to travel to a given distance.
- This corresponds to the loss of energy in units per defined distance.
- This is expressed as an quotient of energy in Newton meters (Nm) and of distance in meters (m). Thus, the rolling resistance is expressed as a force in Newtons (N).
The rolling resistance of a tire is defined by the rolling resistance coefficient cR:
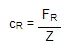
- cR - Rolling resistance coefficient
- FR - Rolling resistance force
- Z - Vehicle weight (sum of all wheel loads)
Goal
- To reduce rolling resistance
- To economize fuel and CO2
Evaluation
- Separated into fuel efficiency classes A to G
- Class D is not used
 Note
Note
- The fuel efficiency classes are listed in EU Regulation (EG) 1222/2009. Tires categories are established by this regulation.
- The rolling resistance is ascertained by prescribed tests performed by the tire manufacturer.
- The lower the rolling resistance, the lower the fuel consumption.
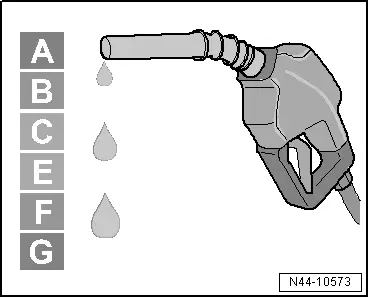
A - Lowest rolling resistance coefficient = lowest fuel consumption
B - + 0.10 liters / 100 km
C - + 0.12 liters / 100 km
E - + 0.14 liters / 100 km
F - + 0.15 liters / 100 km
G - + 0.15 liters / 100 km
Wet Grip
Definition
For the wet grip, the wet grip parameter G must be determined. The wet grip parameter G is defined by testing the distance required by a standardized vehicle to brake from 80 km/h down to 20 km/h on a wet, even road surface. The test is performed using predefined standard reference test tires (SRTT), allowing for the wet grip parameter G to be determined. Mean fully developed deceleration (mfdd) is used for the test.
The mean fully developed deceleration is determined thusly:
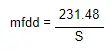
S - the braking distance between 80 km/h and 20 km/h in meters
The wet grip parameter G is determined thusly:

mfdd - mean fully developed deceleration
Goal
- Good wet grip on tire
- Sharp decrease in braking distance
Evaluation
- Separated into wet grip classes A to G
- Classes D and G are not used
 Note
Note
- The wet grip classes are listed in EU Regulation (EG) 1222/2009. Tires categories are established by this regulation.
- The lower the wet grip parameter, the shorter the braking distance.
A - lowest wet grip parameter = shortest braking distance
B - 3 to 6 m longer braking distance compared to category A
C - 3 to 6 m longer braking distance compared to category B
E - 3 to 6 m longer braking distance compared to category C
F - 3 to 6 m longer braking distance compared to category E
1 - When emergency braking at 80 km/h, the difference between using class A and class F tires can be more than 18 m.
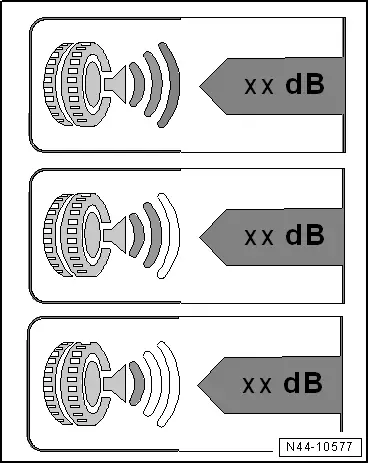
Noise Emission
Goal
- To reduce pass-by noise
- To reduce noise impact
Evaluation
- Take measurements from outside of the vehicle only
- Divided into three classes
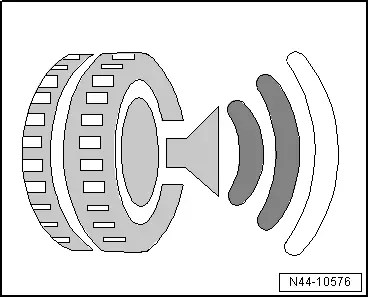
- Three black waves signify the worst performance. The tire produces external rolling noise, which falls below the current EU Directive 2001/43/EG limit. The limit surpasses the future limit set by EU Regulation (EG) 661/2009, which will go into effect in 2016.
- Two black waves: the tire noise level does not exceed the future limit set by EU Regulation (EG) 661/2009, which will go into effect in 2016.
- One black wave: the tire noise level does not exceed the future limit set by EU Regulation (EG) 661/2009, which will go into effect in 2016, by at least three decibels.
 Note
Note
- Reducing the noise measured value from two black waves down to one corresponds to 3 dB, which halves the noise level.
- Please note that extreme tire rolling noise does not always correspond to the noise in the vehicle interior.