Audi Q3: Tires, Air Loss
If the customer complains of loss of air from a tire, the tire must absolutely be checked for embedded foreign debris.
 Note
Note
No repair should be attempted on steel belted tires of which the structure has been punctured by a foreign body.
Corrosion can develop on the steel wires. This will always lead to the separation of the rubber from the steel belt.
Generally, it cannot be determined when the foreign debris was embedded. Therefore, the tire structure may already have been damaged due to driving with insufficient tire pressure.
Damaged belt wires will lead to separation of the rubber from the steel belt sooner or later. As a result, the tire can fail completely after a certain running time, long after the tire damage has occurred.
Tire damage caused by foreign debris is not covered by warranty.
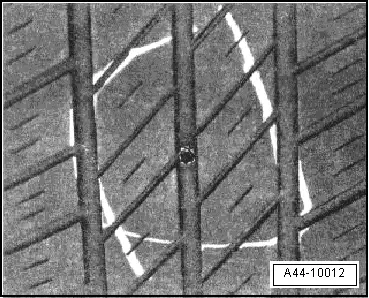
Mounting Damage
Bundle broken during tire inflation.
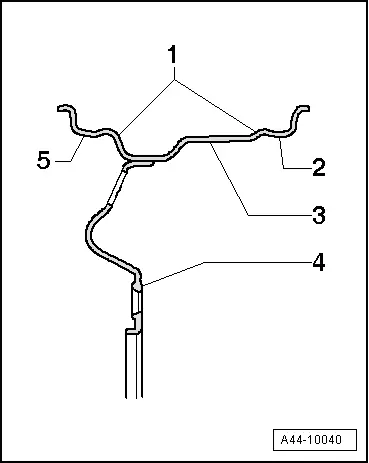
Modern radial car tires are mounted only on safety rims. These have a hump -1- running along the shoulders.
1 - Hump (H2)
2 - Inner bead seat
3 - Rim
4 - Wheel disc
5 - Outer bead seat
The hump prevents the tire from being pressed out of the bead seat during travel with insufficient tire pressure.
When the tire is inflated, the tire bead may not slip completely over the outer rim hump.
In this case, there is the danger that the bead bundle will be overstretched if the tire pressure is too high and the steel wires rupture partially or completely. Torn bundles are often not detectable from outside.
 DANGER!
DANGER!
- Tires with damaged bead bundles are not seated safely and securely on the rim. Such tires are a safety risk!
- In addition, there is the danger that a partially broken bundle tears during continued operation and the tire suddenly tears open. If the bead bundle breaks during inflation, the shell will also be destroyed.
Bead Damage Caused by Tire Changers
The following mistakes when fitting tires can lead to severe tire damage.
- When rolling in the upper bead on the tire changer, the opposing tire bead does not lie completely in its bed.
- The mounting head was adjusted incorrectly.
- The edge of the fitting roller rolls onto the bead.
- The guide rollers are worn or have sharp edges.
Frequently, mounting and run out marks from the guide rollers are identified in the damaged area.
 Note
Note
Both tire beads as well as the bead seats must always be coated with fitting paste.
If mounting damage is undetected, there is the danger that the tire will fail later when driving.
THEREFORE!
- Never fit a tire without fitting paste.
- Do not inflate the bead seating pressure above 3 bar (43.5 psi).
- Do not inflate the tire filling pressure above 4 bar (58 psi).
- After the tire has been fitted, reduce the air pressure to the specified value.
Tire Pressure
Air pressure must be checked regularly. It is recommended to check the tire pressure every 14 days. The correct tire pressure is especially important during long trips or if a load must be carried. A sporty driving style also requires correct or even slightly increased air pressure.
Tires, Damage from Low Tire Pressure
The most common causes of failure are small external damage, a defective valve or a leaky rim due to corrosion or damage.
Strong heating due to driving with substantially low pressure leads to overheating and subsequent separation of shell from rubber.
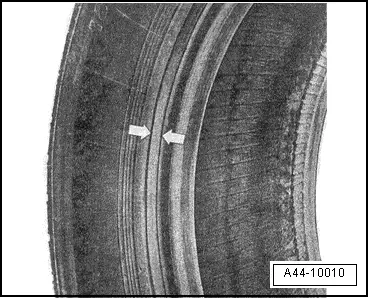
The tire shown here was sporadically driven with tire pressure insufficient for the load. Typical indications for this are the circumferential abrasions in the area of the bead caused by the rim flange and the discoloration. Small, furrowed folds are visible along the inner sidewall.
When the tire rolls, strong shear forces develop between the steel belt layers, especially at the ends of the belts.

Wide furrows along the circumference in the area of the bead indicate that the tire was driven with insufficient air pressure.
Driving a vehicle with insufficient tire pressure or ignoring or not recognizing tire damage can have serious consequences.
The tire can no longer withstand the forces developing during travel.
The function of the tire is limited by the defects mentioned above. The rubber compounds separate from one another, resulting in partial separation of tire components up to complete destruction.
Such damage usually develops over a longer period of time. If an already damaged tire is exposed to high stress, the centrifugal force at higher speeds can tear components off the tire.
Slow Loss of Air Pressure
The slow loss of tire pressure is an especially tricky process because even experienced drivers often do not notice it.
The insufficient air pressure and the related increase in force required to flex the tire (inner friction) cause the tire material to heat up so much that the various components and rubber compounds can separate.
The final stage is usually the complete destruction of the tire.
The cause for the slow pressure loss cannot always be determined because the tire is severely damaged and components of the tire are missing.
The following pages show tires that were destroyed by driving with low tire pressure.
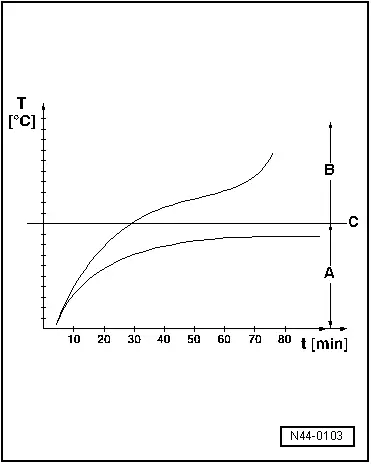
Tire Temperature, Rising When Tires Pressure Is Too Low
The diagram shows the temperature behavior of a tire at 180 km/h (112 mph).
A - Normal range. When maintaining the specified tire pressure, the temperature remains stable
B - Danger zone. When the air pressure is 0.3 bar (4.35 psi) below specification, the temperature rises to above 120º C (32º F) at higher speeds
C - Critical temperature limit. The tire defect is triggered
T - Temperature
t - Driving time in minutes
Cracked Tires
Applies to cracks on tires or tread blowouts and tire breaks.
It is not possible to bill for damage to external effects.

